Sinus tachycardia rhythm strip 192707-How to tell difference between svt and sinus tachycardia
Jan 02, 18 · Sinus bradycardia is the opposite of sinus tachycardia and happens when your sinus node doesn't send enough impulses, resulting in(Rhythm strip)(Rhythm strip) ECG • 12 ldECGlead ECG ECG t i – Complete • ECG strip – Limited information information Rt hth • Rate, rhythm, axis, hth • Rate, rhythm, Ischemia – Easy to get • Sinus node reentry, Inappropriate sinus tachycardia Æพบได ไม บ อยDec , 17 · The sinus rhythm is a bit irregular toward the end of the strip There are probably many things a more advanced practitioner could say about this strip, but it usually requires more than one or two leads to do a complete evaluation For your basic student, it is a good example of sinus rhythm with ventricular bigeminy
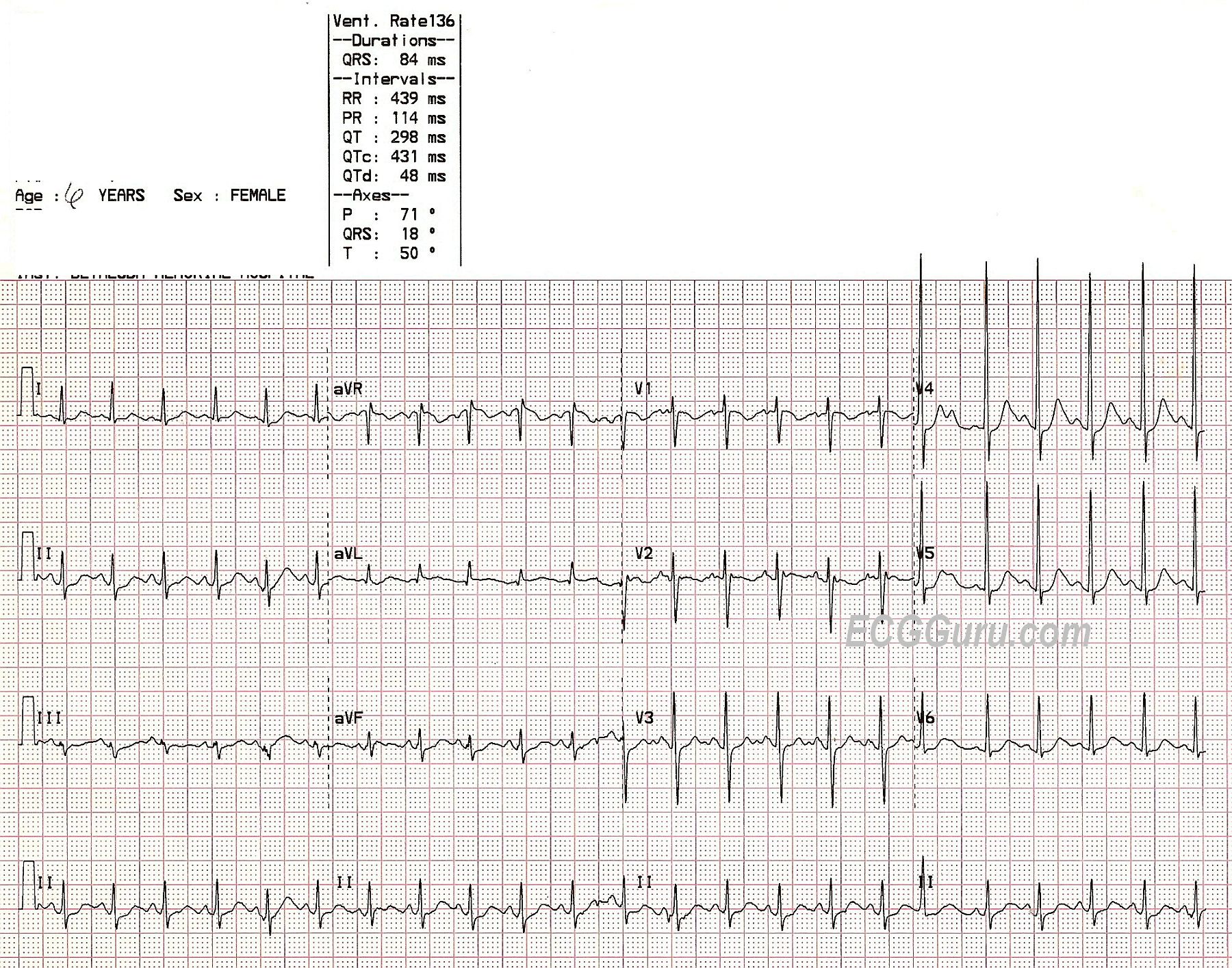
Sinus Tachycardia In A Child Ecg Guru Instructor Resources
How to tell difference between svt and sinus tachycardia
How to tell difference between svt and sinus tachycardia-Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice 1 Sinus Brady Arrhythmia The rate is slow and the rhythm is irregular 2 Sinus Brady heart rate is less than 60 3 Normal Sinus Rhythm 4 Normal Sinus Rhythm 5 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Narrow complex tachycardia 6 Sinus Tachycardia heart rate greater than 100 7 Normal Sinus RhythmJun 14, 17 · Sinus tachycardia is recognized on an ECG with a normal upright P wave in lead II preceding every QRS complex, indicating that the pacemaker is coming from the sinus node and not elsewhere in the



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx
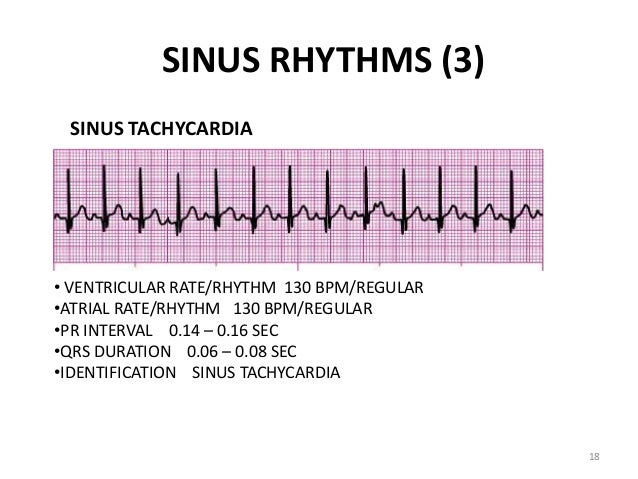
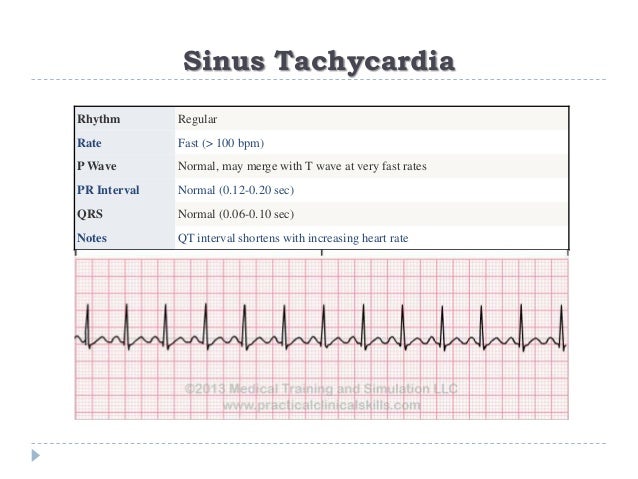
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms 257 5 Sinus Tachycardia Defining Criteria and ECG Features Rate >100 beats/min Rhythm sinus PR ≤0 sec QRS complex normal Clinical Manifestations None specific for the tachycardia Symptoms may be present due to the cause of the tachycardia (fever, hypovolemia, etc) Common Etiologies Normal exerciseFor example sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, accelerated junctional, or ventricular tachycardia Escape Pacemakers The normal electrical flow through the heart originates in the SA node>AV node>Bundle of His> left and right bundle branches> Purkinje fibers where the mechanical cells are stimulatedAug 01, · The middle strip shows adenosine acting on the AV node to suppress AV conduction — there are several broad complex beats which may be aberrantlyconducted supraventricular impulses or ventricular escape beats (this is extremely common during administration of adenosine for AVNRT)
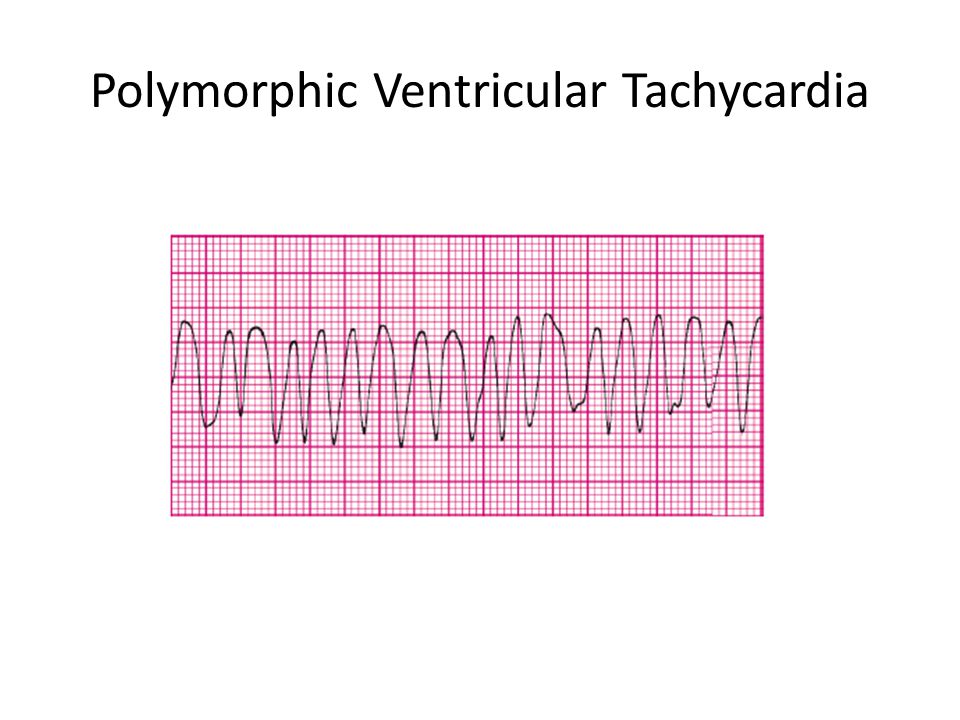
May 16, 21 · The scope of this article is not able to cover ECG interpretation;Rhythm strips on Precourse SelfAssessment with the following matching choices Agonal rhythm/Asystole Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Ventricular Fibrillation Monomorphic Ventricul ar Tachycardia Normal Sinus Rhythm Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Pulseless Electrical Activity Supraventricular Tachycardia SecondDegreePEA occurs when any heart rhythm (other than VTach or V Fib) is observed on the monitor and does not produce a pulse PEA can be any rhythm (sinus, bradycardia, tachycardia) There is organized electrical activity without a pulse
A) Sinus tachycardia with a PVC and ventricular couplet b) Sinus tachycardia with multifocal PV's c) Sinus tachycardia with PV's and PA's d) Atrial fibrillation with uniform PV's 5 An 86yearold woman who experienced a cardiopulmonary arrest The initial rhythm was asystoleMay 05, 15 · A 'supraventricular tachycardia' is a rapid heart rate that originates from above or within the atrioventricular (AV) node It is a blanket term that includes a lot of different rhythms and is simply a starting point on the road to diagnosisA Normal sinus rhythm b Sinus rhythm with a premature junctional beat c Sinus arrhythmia d Sinus rhythm with a premature atrial contraction 8 What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient (from question#7)?




Practice Rhythm Strip 1




Ecg Interpretation Diagnose Any Cardiac Rhythm Nurse Your Own Way
Sinus tachycardia (also colloquially known as sinus tach or sinus tachy) is an elevated sinus rhythm characterized by an increase in the rate of electrical impulses arising from the sinoatrial node In adults, sinus tachycardia is defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats/min (bpm)Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinus rhythm is the normal regular rhythm of the heart set by the natural pacemaker of the heart called the sinoatrial node It is located in the wall of the right atrium Normal cardiac impulses start there and are transmitted to the atria and down to the ventriclesSearch for an EKG strip from a simple drop down list Quickly find any rhythm and click go It will pull up a page with an example strip and an easy to understand deicription No lengthy deep learning No digging Just find your strip fast and easy!




Rhythm Strip From Holter Monitor Showing Bidirectional Vt Wide Qrs Download Scientific Diagram




Basic Dysrhythmias Sinus Arrhythmias Basic Rhythm Strip Interpretation
Oct 25, 17 · In this lesson we're talking about sinus tachycardia and sinus bradycardia, plus a few other special rhythms you'll see from time to time Sinus Tachycardia When the heart is beating at a rate greater than 100 BPM, and the rhythm originates in the SA node, and meets those two criteria listed above, we say that the patient is in "sinus//wwwgofundmecom/f/ninjanerdscienceNinja Nerds,Join us for the next lecture within our ECG playlist We will continue discussing rate and rhythm wiRhythm Strip #2 Heart rate 100 Rhythm Regular P waves One present for each QRS PR interval 14 QRS width08 Interpretation Sinus rhythm/sinus tachycardia Rhythm Strip #2 ECG Criteria Heart rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS width



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead
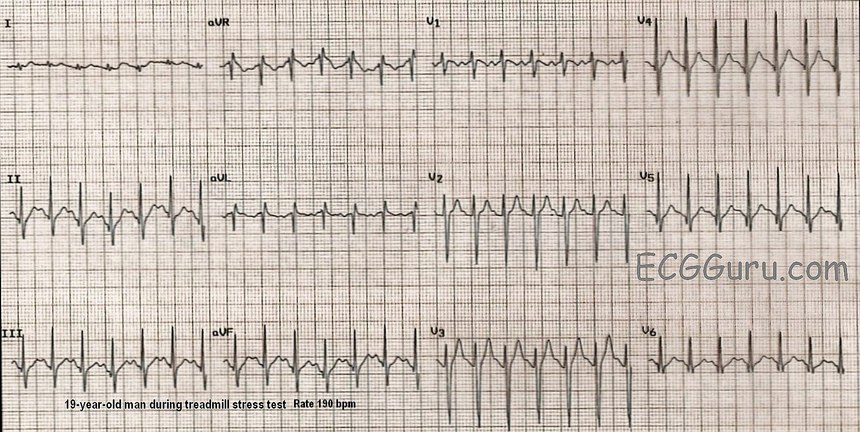



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference
• Interpret a rhythm strip and identify life threatening Normal Sinus Rhythm Rate bpm Rhythm Regular QRS Narrow (Oct 14, · Sinus tachycardia can easily be mistaken for SVT at rapid rates The patient below was brought in via EMS with an identical rhythm strip Because of her fast rate, she was given adenosine The patient clearly has p waves and likely was in sinus rhythm the whole time Remember that the max heart rate is 2 minus the patient's ageThis EKG practice test is designed to help you learn to recoginze all of the EKG rhythms that you will encounter during emergencies and during the AHA ACLS provider course Use these EKG practice tests to help you become proficient in your rapid rhythm identification




Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet



Nt Prophecyhealth Com Docs Manuals Foundations Of Ecg Interpretation1 Pdf
Jan 02, 18 · Normal sinus rhythm typically results in a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute Sometimes, these electrical impulses are sent out faster than normal, causing sinus tachycardia64 year old female patient monitored during cholecystectomy procedure Patient has a history of acute cholecystitis Rhythm analysis indicates normal sinus rhythm (NSR) at 68 bpm Premature atrial complexes (PACs), Premature junctional complexes (PJCs), and Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are presentNov 11, 10 · This wide complex tachycardia could easily be misdiagnosed as V tach However, there are pwaves, and this is a classic RBBB LAFB (left anterior fascicular block) morphology When V tach originates in the left ventricle, there may be an RBBBlike complex, but because VT originates in the myocardium, not in the left bundle (as does RBBB), it




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography
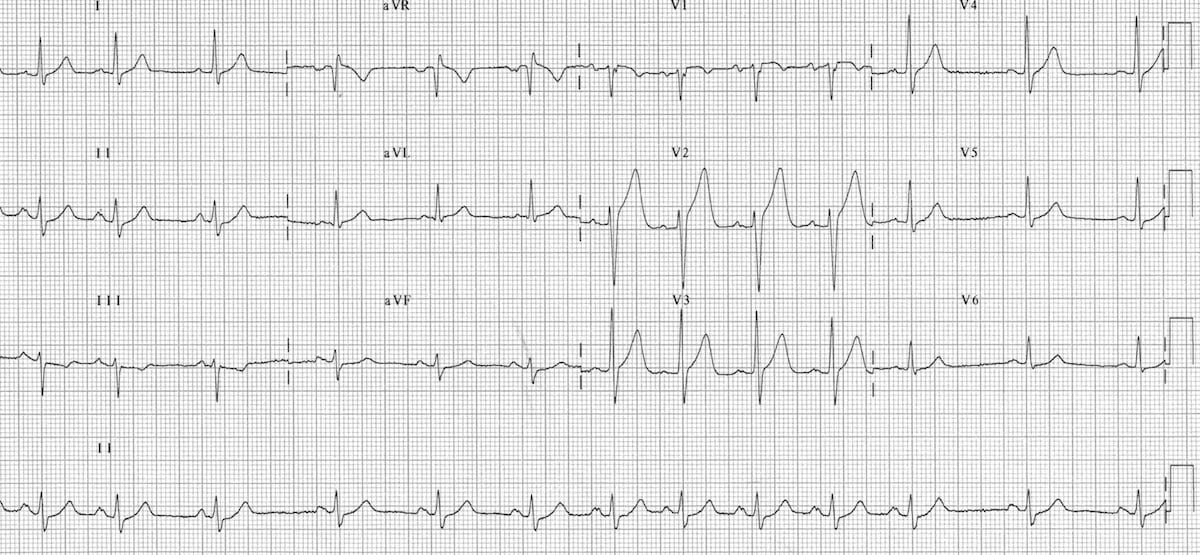



Sinus Arrhythmia Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
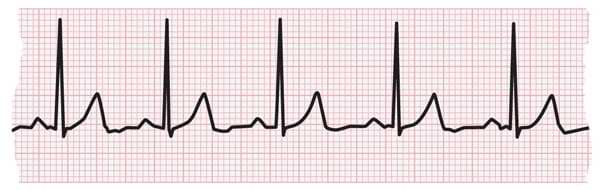
Order e copy of my books from, https//campbellteachingcouk/ebooks/There are only 3 normal cardiac rhythms, sinus rhythm, sinus bradycardia and sinus tachyNov 23, 19 · Sinus tachycardia refers to an increased heart rate that exceeds 100 beats per minute (bpm) The sinus node, or sinoatrial node, is a bundle ofSinus tachycardia is the most common tachyarrhythmia (tachycardia) Sinus tachycardia is the result of an increased rate of depolarization (ie increased automaticity) in the sinoatrial node This simply means that the sinoatrial node discharges electrical impulses at a
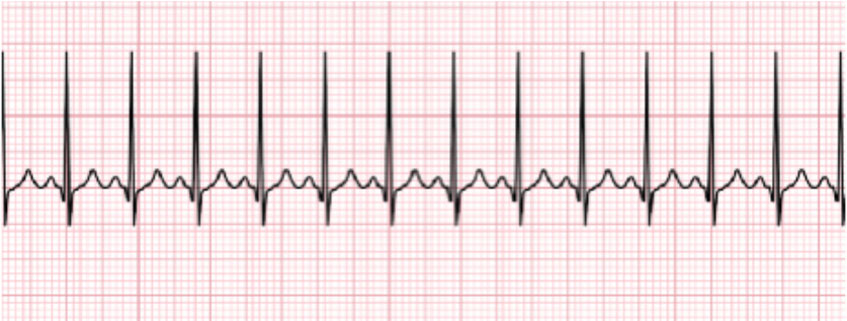



Pals Megacode Sinus Tachycardia




Ekg Normal Sinus Rythms Sinus Bradycardia More Leveluprn
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT) Arrhythmias Heart and Vascular Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is a type of abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia It occurs when a short circuit rhythm develops in the upper chamber of the heart This results in a regular but rapid heartbeat that starts and stops abruptlyApr 30, 13 · "Sinus tachycardia is caused by external influences on the heart, such as fever, anemia, hypotension, blood loss, or exercise These are systemic conditions, not cardiac conditions Sinus tachycardia is a regular rhythm, although the rate may be slowed by vagal maneuvers Cardioversion is contraindicated" 3Supraventricular tachycardia, originating above the ventricles, it can last for seconds to hours Several types of supraventricular tachycardia can be diagnosed Atrial fibrillation, which is a chaotic, fast heart rhythm Fairly common Risk of developing atrial fibrillation increases with age



Www Upstate Edu Hr Document Rhythmstest Pdf



Www Upstate Edu Hr Document Rhythmstest Pdf
Rhythm Strip Samples to help with ACLS Precourse Assessment with Unique Criteria Heart Block Tricks from Terry 1 rhythm strips on precourse assessment with the following matching choices Agonal rhythm/asystole Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Ventricular Fibrillation Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Normal Sinus RhythmAnswer A Explanation Both the atrial and ventricular rates are between 60 and 100 bpm in normal sinus rhythm 11) Identify a rhythm using these criteria regular rhythm, ventricular and atrial rates are 74 beats/minute, P wave precedes each QRS, PR interval and QRS duration within normal limits A) Sinus bradycardiaWhat rhythm would be identified?




Understanding Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet



Acls Ce Part I Of Iii Ecg Strip Interpretation W Case Scenarios Sup
Apr 28, 21 · Arrhythmias on the ECG Rhythm Strip An arrhythmia is any abnormal rhythm other than normal sinus rhythm – the baseline rhythm of the heart This can be a benign variant (like sinus arrhythmia), or it could be deadly (like ventricular fibrillation)Sinus Tachycardia occurs when the rate of electrical impulse formation occurs at a rate exceeding 100 bpm This can occur for a number of different reasons ie diet, stress, illness, response to physical exertion etc The only difference between Normal Sinus Rhythm and Sinus Tachycardia is the rate exceeds 100 bpmMar 12, · Sinus tachycardia is a rhythm in which the rate of impulses arising from the sinoatrial (SA) node is elevated Sinus tachycardia is most often a normal and physiologic response, for example during exercise However, sinus tachycardia can in some instances be inappropriate or pathologic



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf




Atrial Tachycardia Rythms Categorised As Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Svt Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Cardiology Teaching Package Practice Learning Division Of Nursing The University Of Nottingham
Sinus Tachycardia is characterized by a pulse rate of more than 100 beats per minute in adults The electrical signals originate in the sinoatrial (SA) node Appropriate sinus tachycardia can result from exercise, alcohol or caffeine, drugs and anxiety Inappropriate Sinus TachycardiaSinus Tachycardia Sinus tachycardia is sinus rhythm with a rate of > 100bpm Sinus tachycardia is an example of a supraventricular rhythm In sinus tachycardia the sinus node fires between 100 and 180 beats per minute, faster than normal The maximal heart rate decreases with age from around 0 bpm to 140 bpmThe caregiver's ability to interpret ECG strips is assumed Below, we will discuss narrowcomplex versus widecomplex tachycardia, but for now, just know that a widecomplex tachycardia gets worrisome once it's faster than 150 bpm




Atrial Tachycardia Rythms Categorised As Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Svt Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Cardiology Teaching Package Practice Learning Division Of Nursing The University Of Nottingham




How To Identify Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Stripe Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Findings Ecg Questions Youtube
Jul 08, · An EKG strip with sinus tachycardia will show a regular heart rhythm with consistent distances between R waves and P waves P waves will be upright, the PR interval will be normal and the QRS complex will be narrow There will also be a QRS complex for every P waveAccelerated Idioventricular Rhythm Slow VT ECG (Example 3) Bidirectional Ventricular Tachycardia ECG Monomorphic NonSustained Ventricular Tachycardia ECG (Example 1)Competing sinus and idioventricular pacemakers are present There is underlying sinus arrhythmia, with sinus capture occurring when the sinus rate exceeds the idioventricular rate This patient was a healthy 36year old marathon runner with presumably very high resting vagal tone causing sinus bradycardia and sinus arrhythmia



Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikipedia




Ecg Review Sinus Tach Into Psvt 06 08 15 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing
A Call the Rapid response team (if on telemetry), do vagal maneuversAn ECG strip that showed a regular rhythm, an atrial rate greater than the ventricular rate, a constant PRI and two P waves for each QRS complex, and the a QRS is seconds;Rhythm Strip #12 Heart rate 70 Rhythm Regular P waves One present for every QRS PR interval28 QRS width08 Interpretation Normal sinus rhythm, 1st degree AV block Rhythm Strip #12 ECG Criteria Heart rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS width
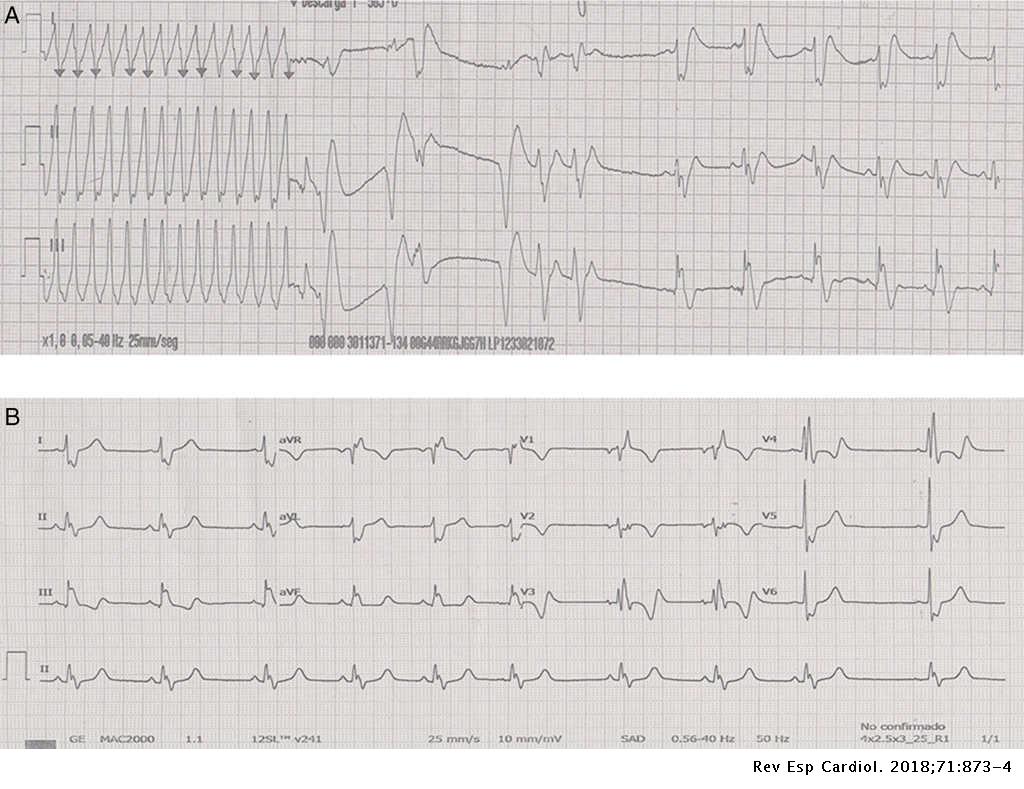



Sustained Ventricular Tachycardia After Thoracic Traumatism In A Patient With Repaired Tetralogy Of Fallot Revista Espanola De Cardiologia



10 Tips To Diagnose Atrial Flutter On An Ekg
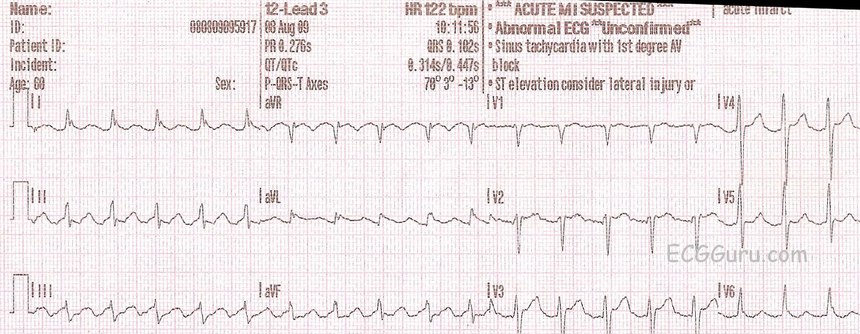
Oct 09, · The Patient The details of this patient's complaints and presentation are lost, but we know he was a 66yearold man who was being treated in the Emergency Department His rhythm went from sinus tachycardia with nonrespiratory sinus arrhythmia to multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) to widecomplex tachycardiaRhythm analysis indicates sinus tachycardia at over 100 bpm First degree heart block is also present This encounter shows a fast rate over 100 bpm, with a regular rhythm and P waves, indicating sinus tachycardia The extremely long delay between the P wave and QRS indicates first degree heart block



Tachycardia Fast Heart Rate American Heart Association
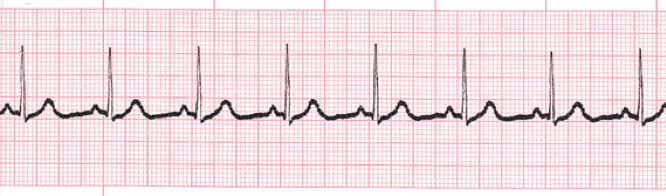



Normal Sinus Rhythm Training Acls Cardiac Rhythms Video Proacls




Ekg Normal Sinus Rythms Sinus Bradycardia More Leveluprn
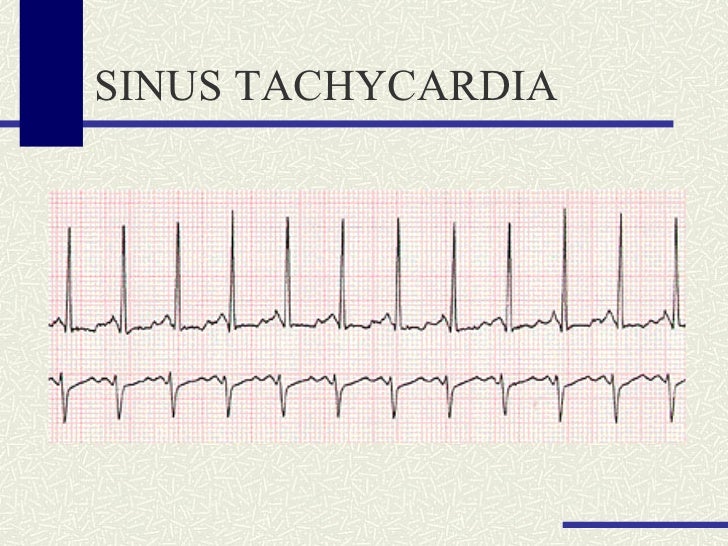



Basic Rhythm Strip Review




Supraventricular Tachycardia Wikipedia
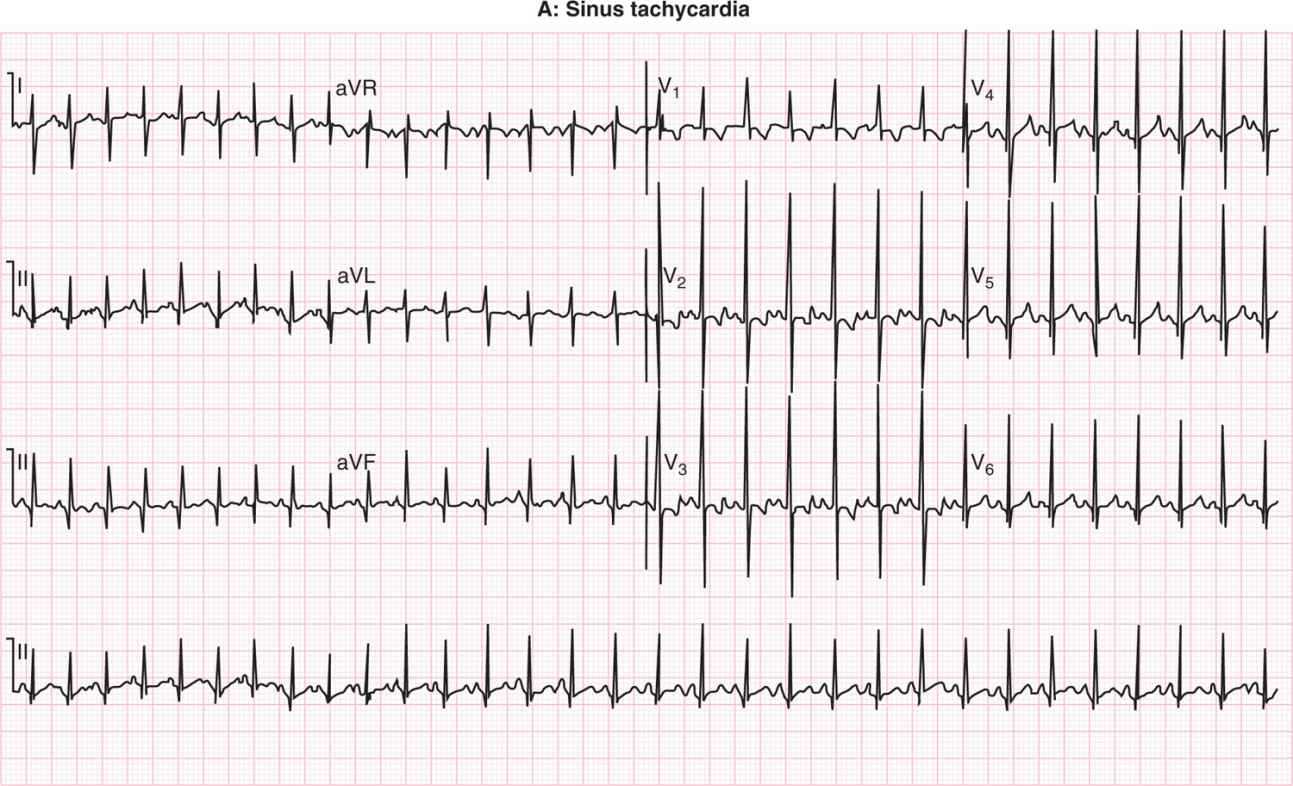



Neonatal Arrhythmias Obgyn Key
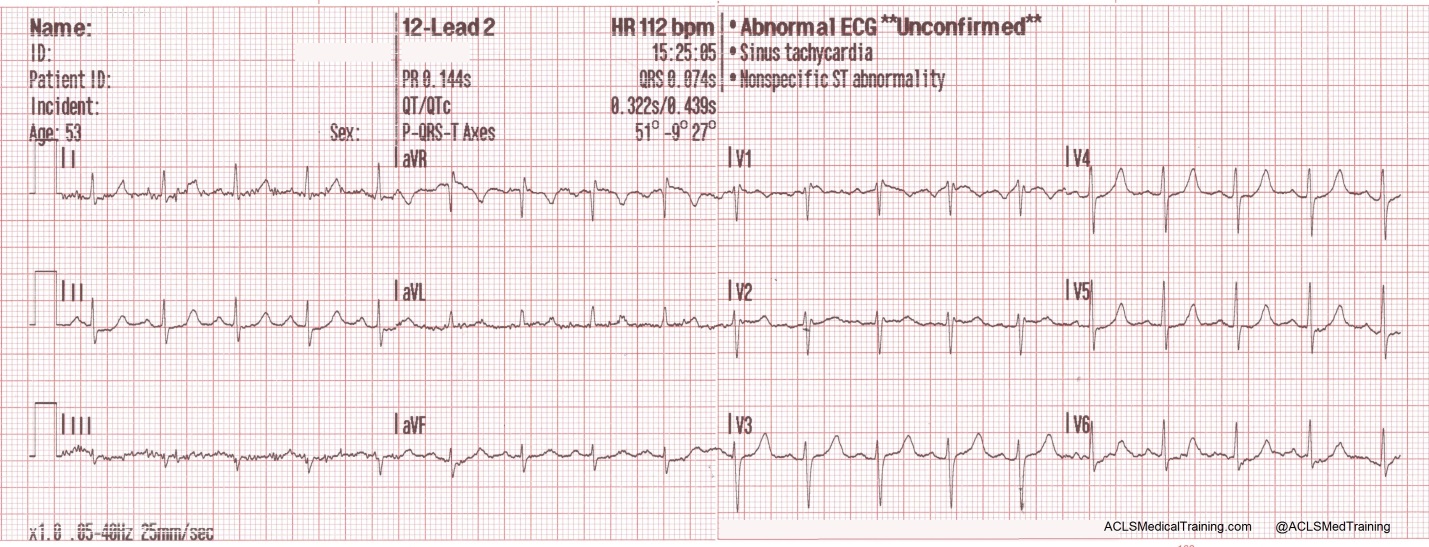



Treating Supraventricular Tachycardia With Adenosine



1




Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia With Block Ectopic Atrial Tachycardia With Block Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx
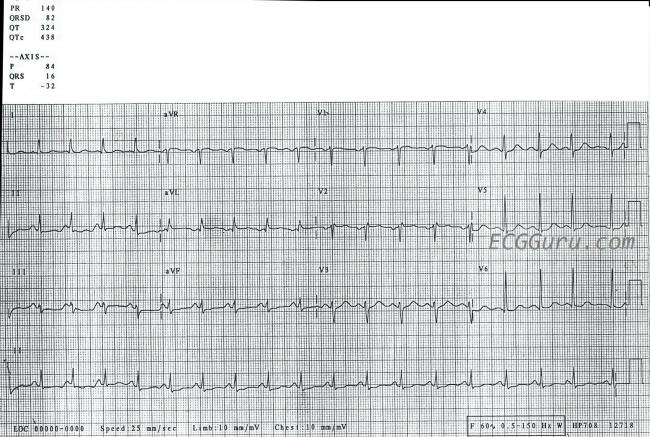



Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Cv Physiology Abnormal Rhythms Definitions



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Telemetric And Ecg Holter Warehouse Project



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice



Ecg Or Ekg Sample Strips Ms Cardiovascular



Acls Rhythms Cheat Sheet Ppt Video Online Download



Lesson V Ecg Rhythm Abnormalities
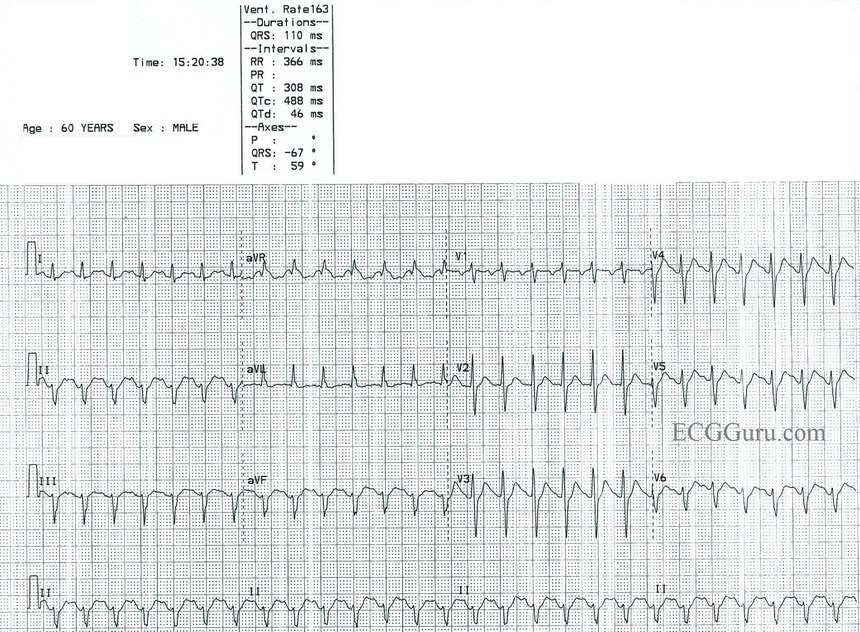



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference




Sinus Tachycardia In A Child Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



No Doubling The Paper Speed Will Not Reveal Hidden P Waves Ems 12 Lead




Pin On Ecg Ekg Rhythm Strips
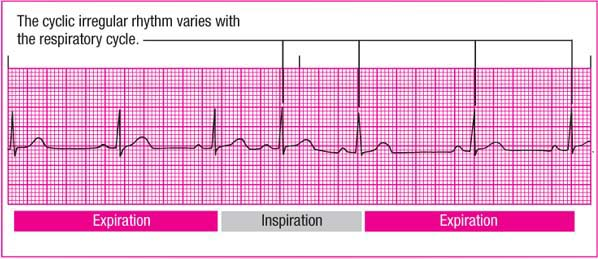



Sinus Node Arrhythmias Anesthesia Key




Ekg Atrial Flutter Rush Emergency Medicine



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead
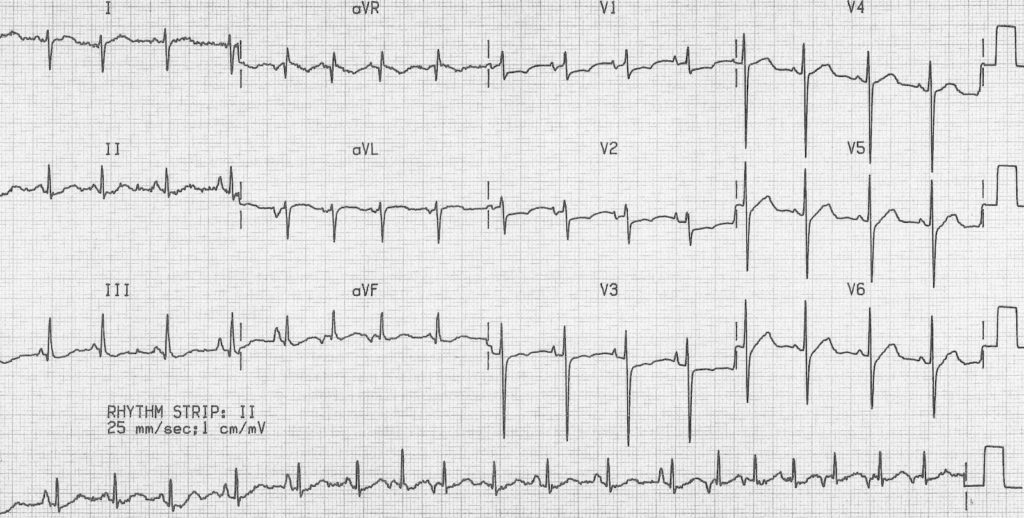



Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Mat Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Ekg Normal Sinus Rythms Sinus Bradycardia More Leveluprn




Interpret Ekgs Strips Like A Boss Nursing Com




Sinus Bradycardia Wikipedia
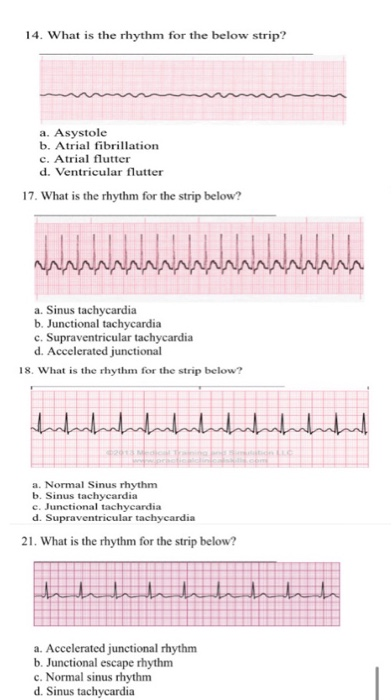



14 What Is The Rhythm For The Below Strip A Chegg Com




Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia Mistaken For Relapse Of Reentrant Supraventricular Tachycardia In A Young Woman Treated Successfully With Ivabradine



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf



Arrhythmia Recognition The Art Of Interpretation




Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia With Block Ectopic Atrial Tachycardia With Block Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 653 Rhythms For Acls




Atrial Tachycardia Rythms Categorised As Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Svt Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Cardiology Teaching Package Practice Learning Division Of Nursing The University Of Nottingham



Med Virginia Edu Emergency Medicine Wp Content Uploads Sites 232 15 10 Introduction To Ecg Rhythms Pdf




Sinus Tachycardia Definition Features



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Ecg Review 1 Av Block In Lead V1 01 12 15 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing
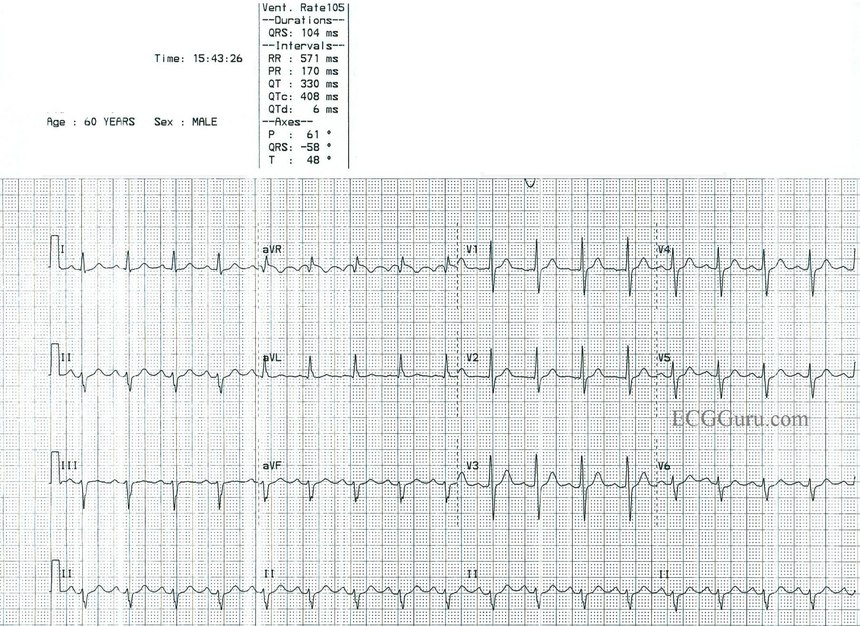



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference



1
.JPG)



Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 40 Regular Svt List 1 Flutter Psvt Sinus Tachycardia Vagal Maneuver




Ventricular Tachycardia Hd Stock Images Shutterstock



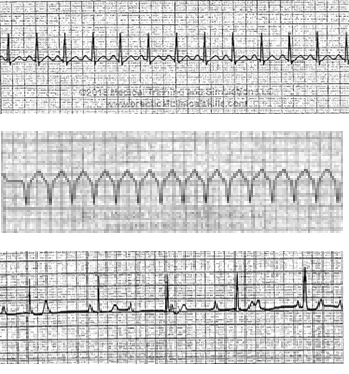
Treating Supraventricular Tachycardia With Adenosine



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead
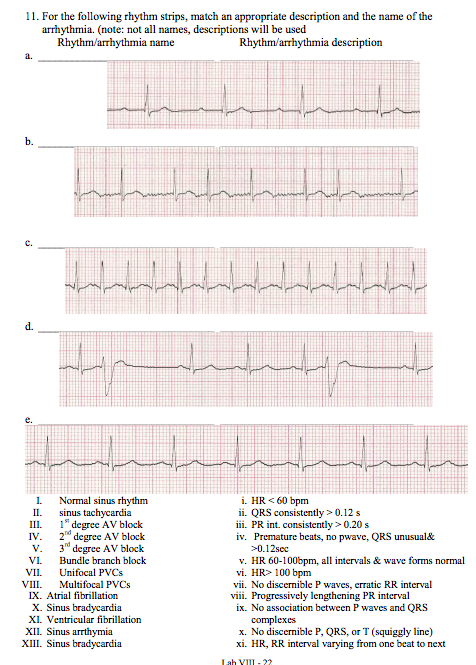



11 For The Following Rhythm Strips Match An Chegg Com




Sinus Tachycardia Vs Sinus Bradycardia Vs Sinus Arrhythmia
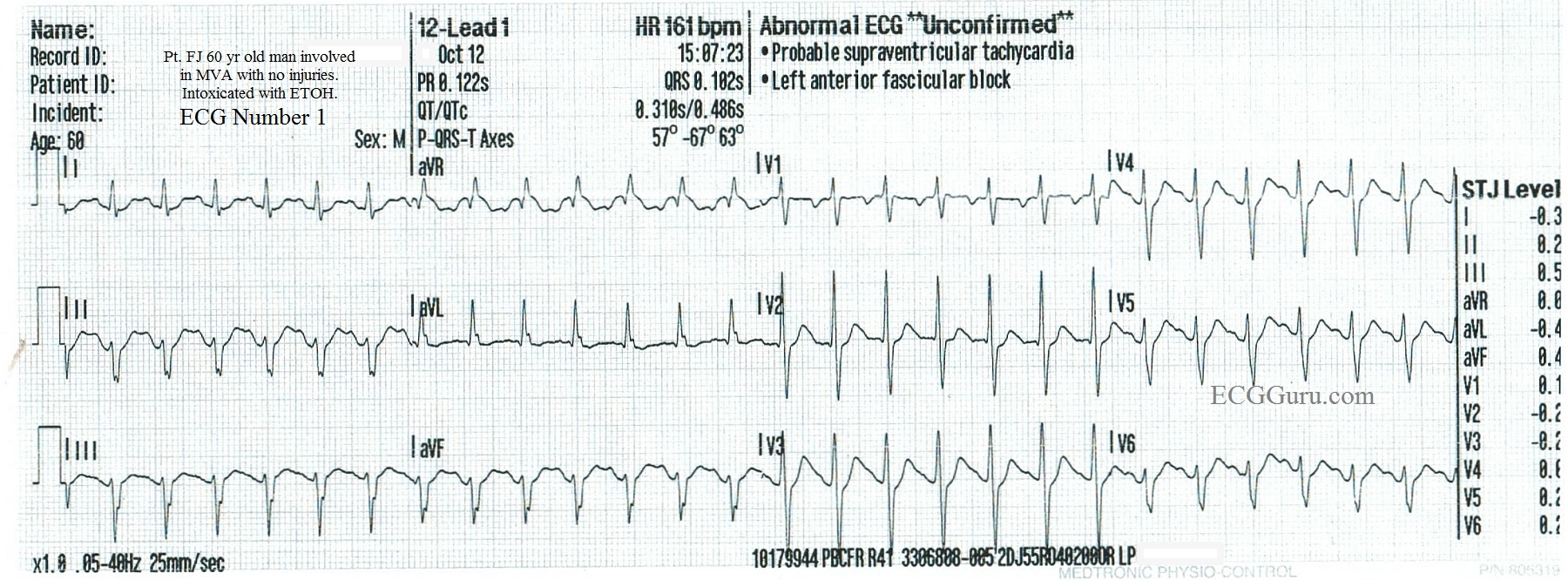



Sinus Tach Vs Svt In An Inebriated Patient Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



3




Ecg Learning Center Test



Www Upstate Edu Hr Document Rhythmstest Pdf



Please Match The Ekg Strips A Normal Sinus Rhythm B Chegg Com




Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 72 Sinus Tachycardia In A Child Juvenile T Wave Variant Baseline Wander Artifact



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Practice Test Only Dysrhythmia Interpretation Therapeutic Modalities Pdf Free Download
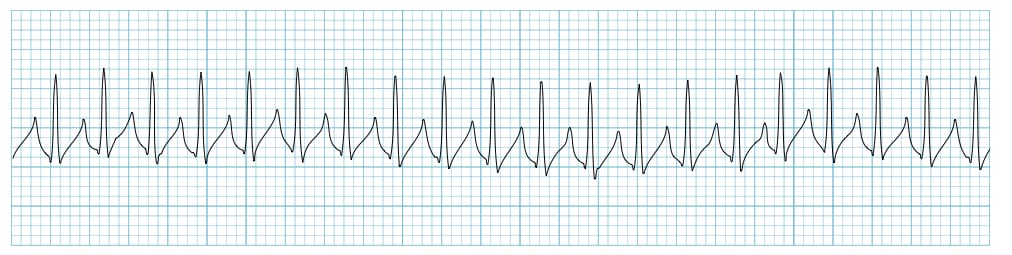



Supraventricular Tachycardia Svt Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Assessment Of Arrhythmias



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead
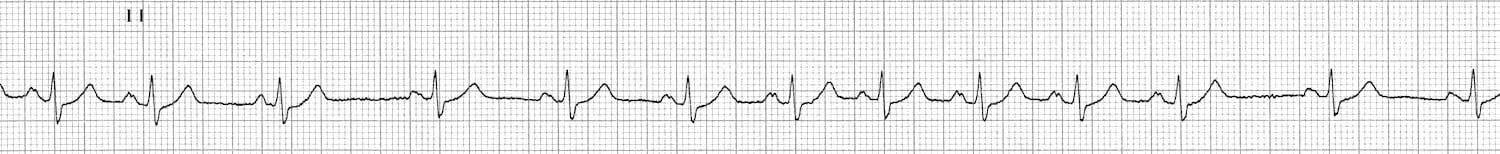



Sinus Arrhythmia Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
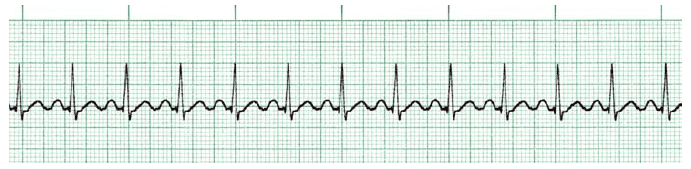



Acls Rhythms Practice Test Recognition Rhythm Strips Pdf



1



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Pin On Cath Lab




The Rhythm Strip In Coronary Care Unit The Sinus Tachycardia Arrow Download Scientific Diagram




Pin On Hemo



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx
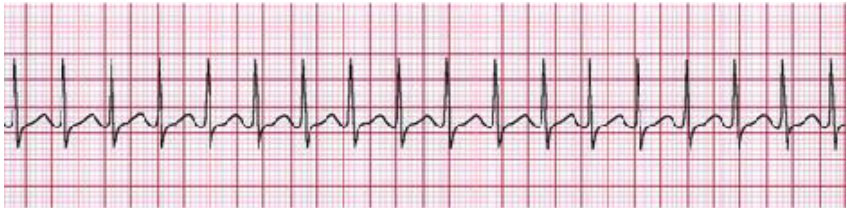



Pals Megacode Sinus Tachycardia




Differential Diagnosis Of Wide Qrs Complex Tachycardias The Cardiology Advisor



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf




7 Lead Rhythm Strip Showed Artifact With Normal Sinus Rhythm In Lead I Download Scientific Diagram
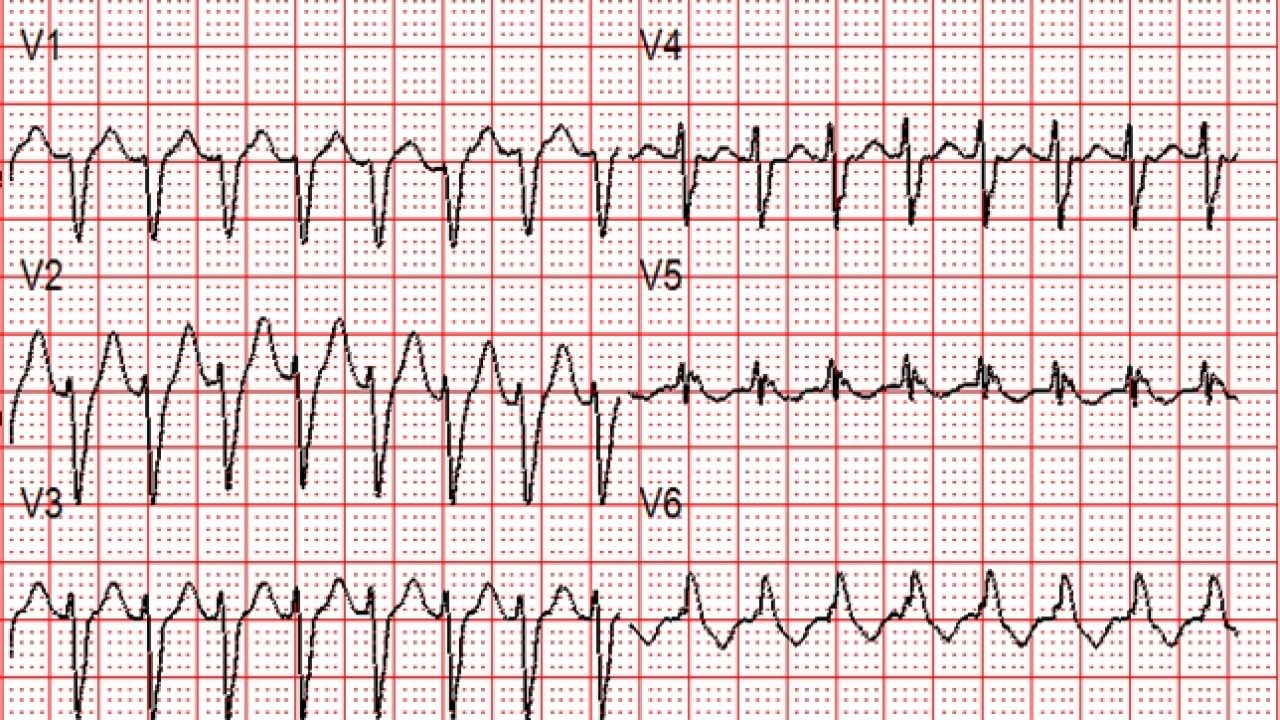



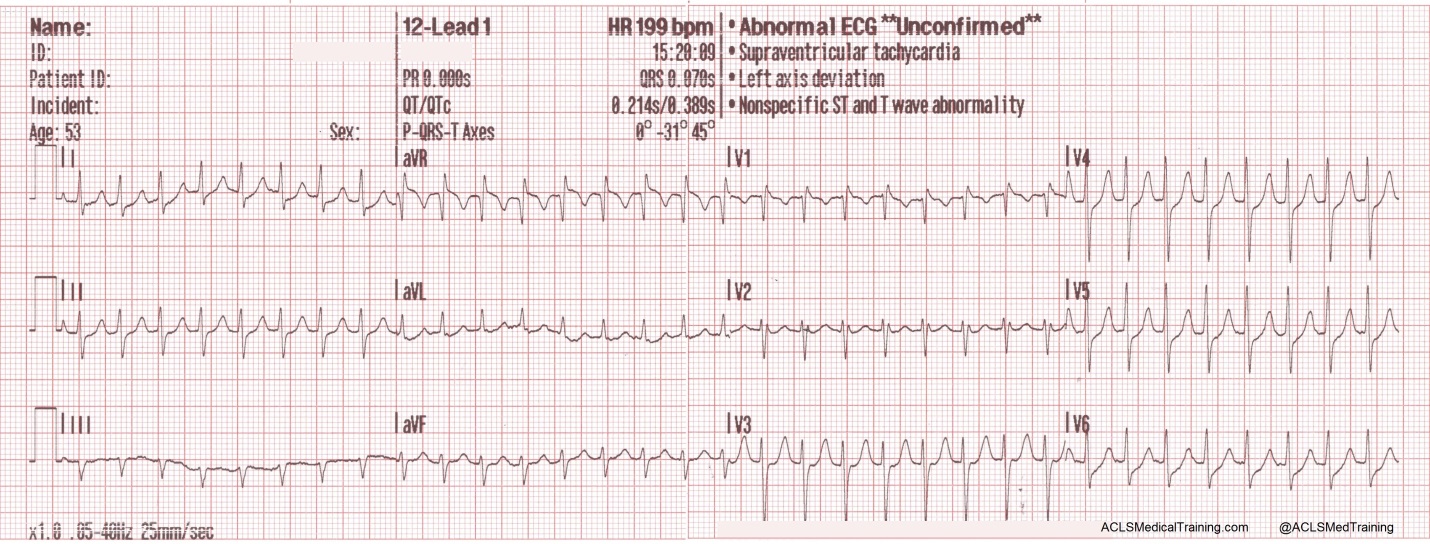
Svt With Aberrancy Or Ventricular Tachycardia Acls Medical Training



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice



The Whole Ecg A Really Basic Ecg Primer



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead



Ecg A Pictorial Primer Medicine On Line Com
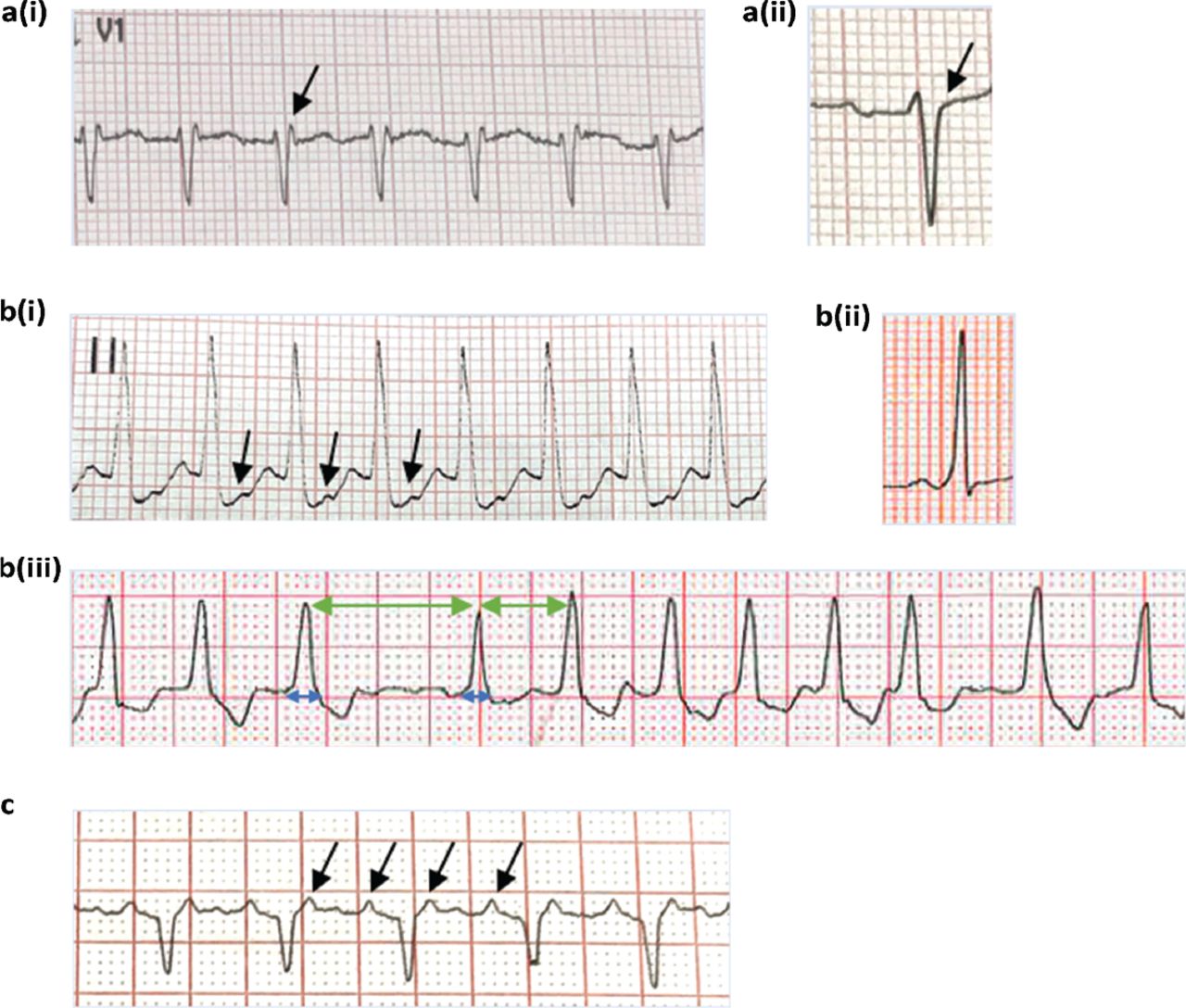



Supraventricular Tachycardia An Overview Of Diagnosis And Management Rcp Journals




Sinus Tachycardia Cute766




Mahaim Tachycardia And Intravenous Adenosine Heart


コメント
コメントを投稿